What world popular Institutions and Organizations have said about spirulina?
Spirulina- was declared by the United Nations World Food Conference of 1974 as the best food for the future.

“There is a need for both national governments and inter-governmental organizations to re-evaluate the potential of Spirulina to fulfil both their own food security needs as well as a tool for their overseas development emergency response efforts” – The UN-Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) Report on Spirulina 2008.
“For WHO, Spirulina represents an interesting food for multiple reasons, rich in iron and protein, and is able to be administered to children without any risk. We at WHO consider it a very suitable food.” – United Nations World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland June 8Th, 1993
Common Health Benefits of Spirulina
1. Spirulina Is Extremely High in Many Nutrients
2. Act as a immune Enhancer
3. Powerful Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
4. Can Lower “Bad” LDL and Triglyceride Levels
5. Protects “Bad” LDL Cholesterol From Oxidation
6. Have Anti-Cancer Properties
7. Reduce Blood Pressure
8. Improves Symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis & Inflammation
9. Effective Against Anemia
10. May Improve Muscle Strength and Endurance
11. Aid Blood Sugar Control
12. Have Anti-Aging Properties
13. Protects the skin by providing elasticity
14. Have Anti-Asthma Properties
15. Recommended in Pregnancy & Overall Child development
16. Protect your eyes from damage due to ultraviolet-induced
17. Effective in weight management
Spirulina Proteins & Vitamins
Protein: Highest natural source of protein up to 70%
Digestibility: Upto 98%
Complete protein: Presence of 18 amino acids including all 9 Essential Amino acids
| Essential | g/100g |
| Histidine | 0.5-1.5 |
| Isoleucine | 3.0-4.0 |
| Leucine | 3.0-5.0 |
| Lysine | 3.0-6.0 |
| Methionine | 1.0-6.0 |
| Phenylalanine | 2.5-3.5 |
| Threonine | 1.5-3.0 |
| Tryptophan | 1.0-2.0 |
| Valine | 1.0-3.5 |
| Non-Essential | g/100g |
| Alanine | 4.0-5.0 |
| Arginine | 3.0-5.0 |
| Aspartic acid | 1.50-3.0 |
| Cystine | 0.50-0.75 |
| Glutamic acid | 6.0-9.0 |
| Glycine | 2.0-4.0 |
| Proline | 2.0-3.0 |
| Serine | 3.0-4.5 |
| 1.0-3.1 | 1.0-3.0 |
| Vitamins | mg/100g |
| Provitamin A | 2.330 IU/kg |
| (β-carotene) | 140 |
| Vitamin E | 100 α-tocopherol equiv. |
| Vitamin K | 2.2 |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | 2.5-5.0 |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 4.0-7.0 |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 3.0-6.0 |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | 0.1 |
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | 0.005 |
| Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid) | 0.05-0.3 |
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | 0.05-0.2 |
Role of Essential Amino Acids:
| ISOLEUCINE: | Used for energy by muscle tissue, forms haemoglobin | ||||||||
| LEUCINE | Increase cognitive functions of brain, reduces muscle protein breakdown. | ||||||||
| LYSINE | Adequate absorption of calcium, helps form collagen, aids in the production of antibodies, hormones. | ||||||||
| METHIONINE: | Prevents disorders of the hair, skin and nails, lowers cholesterol levels, reduces liver fat and protects the kidneys. | ||||||||
| PHENYL-ALANINE | Stimulates metabolic rate and required by the thyroid gland, produces norepinephrine. | ||||||||
| THREONINE | Prevents fat build-up in the liver, assists digestion & metabolism | ||||||||
| TRYPTOPHAN | Natural relaxant, treatment of migraine headaches, works with lysine in reducing cholesterol levels. | ||||||||
| VALINE | Promotes mental vigor, muscle coordination andand calm emotions. | ||||||||
| HISTIDINE: | Restore tissues in the body and sustaining the myelin sheaths which shield the nerve cells. production of the red and white blood cells and protection from eczema. | ||||||||
Role of Non Essential Amino Acids:
| ALANINE | Strengthens cellular walls | ||||||||
| ARGININE | Important to male sexual health as seminal fluid is 80 percent arginine. Also helps detoxify the blood | ||||||||
| ASPARTIC ACID | Aids transformation of carbohydrates into cellular energy. | ||||||||
| CYSTINE | Aids pancreatic health, which stabilizes blood sugar and carbohydrate metabolism. Has been used to alleviate some symptoms of food allergy and intolerance. | ||||||||
| GLUTAMIC ACID | With glucose, one of the principal fuels for the brain cells. Has been used to reduce the craving for alcohol and stabilize mental health. | ||||||||
| GLYCINE | Promotes energy and oxygen use in the cells. | ||||||||
| PROLINE | A precursor of glutamic acid | ||||||||
| SERINE | Helps form the protective fatty sheaths surrounding nerve fibers. | ||||||||
| TYROSINE | Slows aging of cells and suppresses hunger centers in the hypothalamus. Can be synthesized from phenylalanine. Involved in proper coloration of hair and skin, including protection from sunburn. | ||||||||
Role of Vitamins:
| Vitamin A | Needed for vision, healthy skin and mucous membranes, bone and tooth growth, immune system health | |||||||||
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant; protects cell walls | |||||||||
| Vitamin K | Needed for proper blood clotting | |||||||||
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism; important for normal vision and skin health | |||||||||
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism; important for nervous system, digestive system, and skin health | |||||||||
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) | Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism | |||||||||
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | Part of an enzyme needed for protein metabolism; helps make red blood cells | |||||||||
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism | |||||||||
| Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) | Part of an enzyme needed for making DNA and new cells, especially red blood cells | |||||||||
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Part of an enzyme needed for making new cells; important to nerve function | |||||||||
Spirulina Minerals, Fatty Acids & Phytopigments
| Minerals | mg/100g |
| Calcium | 300-500 |
| Phosphorus | 800-1000 |
| Magnesium | 400-800 |
| Iron | 60-80 |
| Sodium | 500-800 |
| Potassium | 1300-1650 |
| Zinc | 2.0-4.0 |
| Copper | 1.0-2.0 |
| Manganese | 1.0-3.0 |
| Chromium | 0.2-0.5 |
| Selenium | 0.05-0.2 |
| Fatty Acids | g/100g |
| Myristic acid | 0.05-0.10 |
| Palmitic acid | 1.0-2.0 |
| Stearic acid | 0.10-0.20 |
| Oleic acid | 0.10-0.20 |
| Linoleic acid | 0.50-0.90 |
| Gamma Linoleic acid | 1.00-1.50 |
| α-Linoleic acid | Trace |
| Stearidonic acid | Trace |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid | Trace |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | Trace |
| Phytopigment | mg/100g |
| Phycocyanin | 15000-19000 |
| Total Carotenoids | 400-500 |
| Carotenes | 160-260 |
| Alpha-carotene | Traces |
| Beta-carotene | 170 |
| Xanthophyls | 170-240 |
| Cryptoxanthin | 55.6 |
| Echinenone | 44 |
| Zeaxanthin | 31.6 |
| Lutein | 29 |
| Chlorophyll | 1300-1700 |
Role of Minerals
| Calcium | Important for healthy bones and teeth; helps muscles relax and contract; important in nerve functioning, blood clotting, blood pressure regulation, immune system health | ||||||||
| Phosphorus | Important for healthy bones and teeth; found in every cell; part of the system that maintains acid-base balance | ||||||||
| Magnesium | Found in bones; needed for making protein, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, immune system health | ||||||||
| Iron | Part of a molecule (hemoglobin) found in red blood cells that carries oxygen in the body; needed for energy metabolism | ||||||||
| Iodine | Found in thyroid hormone, which helps regulate growth, development, and metabolism | ||||||||
| Sodium | Needed for proper fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction | ||||||||
| Potassium | Needed for proper fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction | ||||||||
| Zinc | Part of many enzymes; needed for making protein and genetic material; has a function in taste perception, wound healing, normal fetal development, production of sperm, normal growth and sexual maturation, immune system health. | ||||||||
| Copper | Part of many enzymes; needed for iron metabolism | ||||||||
| Manganese | Part of many enzymes | ||||||||
| Chromium | Works closely with insulin to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels | ||||||||
| Selenium | Antioxidant | ||||||||
Role of Phyto-Pigments
| Calcium | Important for healthy bones and teeth; helps muscles relax and contract; important in nerve functioning, blood clotting, blood pressure regulation, immune system health | ||||||||
| Phosphorus | Important for healthy bones and teeth; found in every cell; part of the system that maintains acid-base balance | ||||||||
| Magnesium | Found in bones; needed for making protein, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, immune system health | ||||||||
| Iron | Part of a molecule (hemoglobin) found in red blood cells that carries oxygen in the body; needed for energy metabolism | ||||||||
| Iodine | Found in thyroid hormone, which helps regulate growth, development, and metabolism | ||||||||
| Sodium | Needed for proper fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction | ||||||||
| Potassium | Needed for proper fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction | ||||||||
| Zinc | Part of many enzymes; needed for making protein and genetic material; has a function in taste perception, wound healing, normal fetal development, production of sperm, normal growth and sexual maturation, immune system health. | ||||||||
| Copper | Part of many enzymes; needed for iron metabolism | ||||||||
| Manganese | Part of many enzymes | ||||||||
| Chromium | Works closely with insulin to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels | ||||||||
| Selenium | Antioxidant | ||||||||
Role of Phycocyanin in Spirulina
| Phycocyanin is a phycobilliprotein that gives Spirulina its unique colour and is believed to be the source of many of Spirulina’s positive actions. | |||||||||
| Phycocyanin is a novel anticancer molecule, which shows potent cancer preventive and cancer fighting properties. | |||||||||
| Phycocyanin also imparts its anti-inflammatory and neuro-protective properties to Spirulina. | |||||||||
| Rich Phycocyanin content in Spirulina demonstrates strong anti-oxidant profile, due to which it is helpful in suppressing unfriendly and drug resistant bacteria like E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas etc, thus cleanses intestinal flora. | |||||||||
| Its anti-oxidant property improves the detoxification process of the body. High Phycocyanin Spirulina also plays a vital role in enhancing the immune system, thus strengthening the body enabling it to ward off infections and may reduce post treatment recovery time. | |||||||||
| Owing to these virtues of Phycocyanin, Hash Biotech Labs has optimised the Spirulina strain for higher Phycocyanin content. |
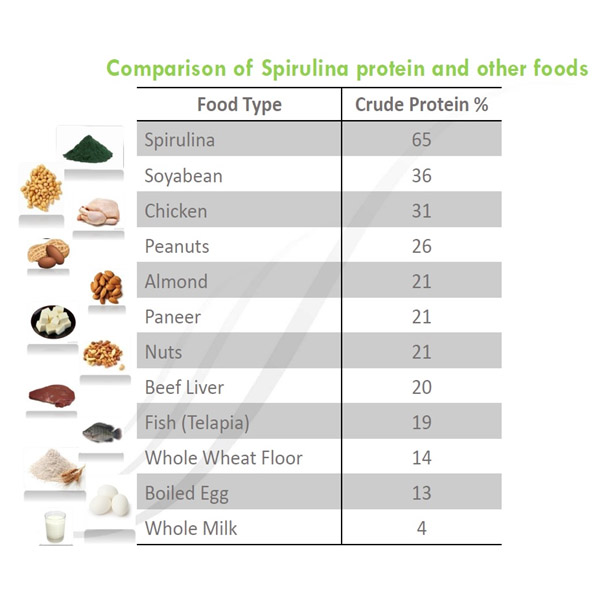
Comparison of Spirulina protein and other foods

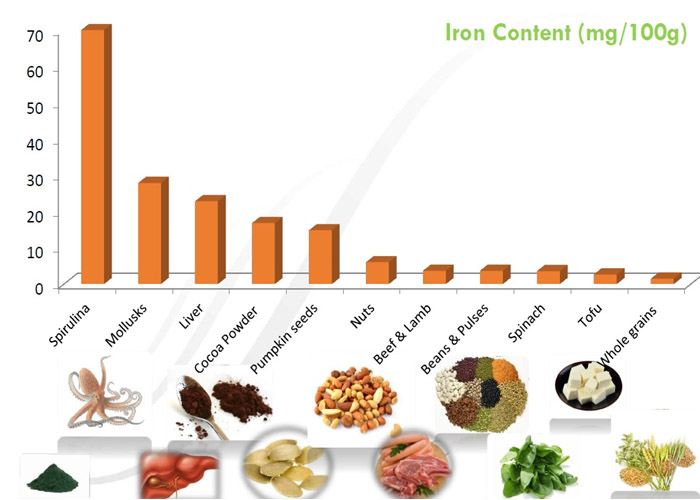
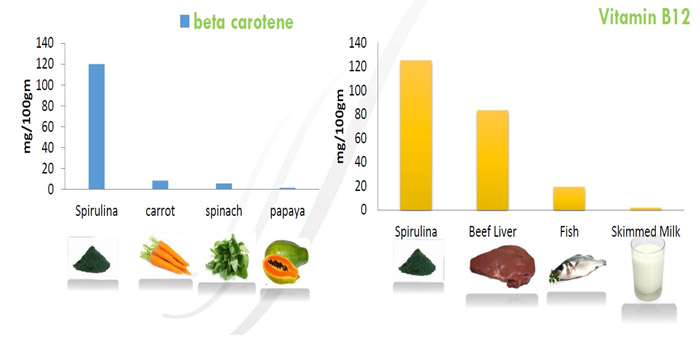
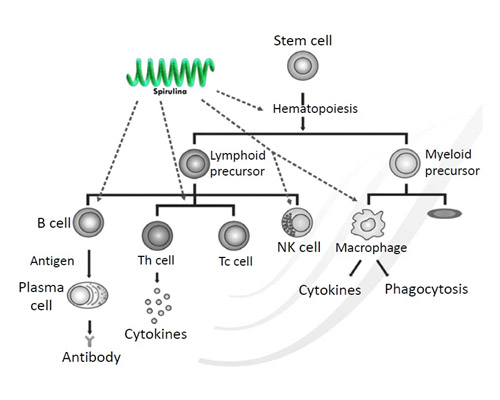
Spirulina as Immunity Enhancer
| ANTIBODY RESPONSE AND MACROPHAGE | |||||||
| Spirulina enhances hematopoiesis to produce more erythrocytes and lymphocytes | |||||||
| Spirulina shows direct effect on innate immunity by activating macrophages and NK cells | |||||||
| Spirulina activates T-helper cells and T-cytotoxic cells | |||||||
| Spirulina induces the maturity of B-cells for the production of antibodies | |||||||
| MUCOSAL IgA RESPONSE | |||||||
| Agglutination of micro-organisms | |||||||
| Neutralization of bacterial enzymes, toxins, and viruses; immune exclusion | |||||||
| Blocking adherence of bacteria to the epithelium | |||||||
| Reduction of antigens or allergen absorption. | |||||||
Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina for Anaemia
| Contains porphyrin and bio-chelated iron which help in curing anemia. | ||||||||||
| High nutrient density, especially the easily assimilated protein, folic acid, vitamin E, blood-building vitamins B12, folic acid and the amino acids, make it an ideal food source for persons suffering from anemia. Its use is most encouraged for expecting and lactating mothers. |
Role of Spirulina in Diabetes
| Spirulina helps to fulfil all the deficiencies, the accumulation of which leads to diabetic condition. | |||||||||
| Possesses hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties and reduces insulin resistance. | |||||||||
| Increases glucose metabolism in Type II diabetic patients | |||||||||
| Activates pancreatic beta cells for insulin production in Type I diabetic patients. | |||||||||
| Stimulate glycogenesis in the liver & Greater uptake of glucose from blood by liver cells (Fayzunnessa et al., 2011). | |||||||||
| Lower risk of the tissues for oxidation stress and high resistance for diabetes (Layam and Reddy et al., 2007). | |||||||||
| Inhibition of endogenous synthesis of lipids & down regulation of lipogenesis. | |||||||||
| Spirulina prevents diabetic retinopathy. | |||||||||
| Spirulina helps to mitigate the effects of unbalanced nutritional condition in diabetic patients. |
Role of Spirulina in Hypertension and Cholesterol
| Spirulina helps in electrolytic balance by providing Potassium to body | |||||||||
| Spirulina boots the synthesis of Nitric Oxide, which helps in dilation of blood vessels, thus in turn improves blood flow through them. | |||||||||
| Spirulina prevents blood clots in arteries by preventing platelets aggregation | |||||||||
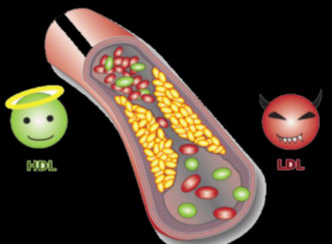
| Spirulina helps in significant reduction in serum cholesterol, blood cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL levels. | |||||||||
| Spirulina increase HDL levels. | |||||||||
| Spirulina reduces hypercholesterolemic Atherosclerosis. |
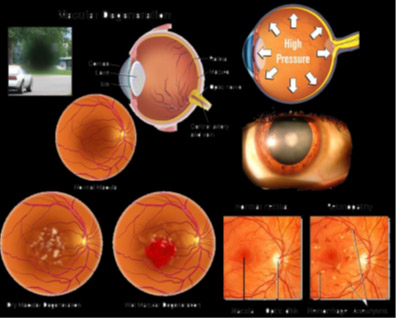
Spirulina for Eye Health
| Spirulina is a rich dietary source of zeaxanthin, a xanthophyll, which are substances similar to carotenes, the proeye compounds. | |||||||||
| Help protect your eyes from damage due to ultraviolet-induced oxidation of lipid membranes and high blood glucose level by slowing down the oxidation and thereby helping prevent degeneration of macula. | |||||||||
| Thus, its intake may have benefit in reducing risk of glaucoma, cataract and age-related macular degeneration. |
Spirulina for Anti-Aging
| Free- radical reactions have been implicated in the pathology of many human diseases. | |||||||||
| A high level of antioxidants present in Spirulina help in neutralisation or scavenging of these free radicals. | |||||||||
| ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) value is about 50 times that of Spinach. |
Antioxidant effects of Spirulina
| Mechanisms of Antioxidant activity of Spirulina | |||||||
| Free radical scavenging | |||||||
| Inhibition of lipid peroxidation | |||||||
| Superoxide anion (an ROS) hydroxyl, alkoxyl, and peroxyl radicals | |||||||
| Reduced Malondialdehyde & conjugated diene | |||||||
| Enhancement of glutathione, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase | |||||||
| Neuro-Hepato-Nephro Protective: | |||||||
| Spirulina’s enriched antioxidant profile helps to protect us from neuro-degenerative diseases like Alzhiemer’s, Parkinson’s and other forms of age related dementia. | |||||||
| Improves overall cognitive functions | |||||||
| Protects the liver and kidney cells from lipid peroxidation and ROS. | |||||||
| Protects liver and kidney cells from metal induced toxicity. | |||||||
Antioxidant effects of Spirulina
| Mechanisms of Antioxidant activity of Spirulina | |||||||
| Free radical scavenging | |||||||
| Inhibition of lipid peroxidation | |||||||
| Superoxide anion (an ROS) hydroxyl, alkoxyl, and peroxyl radicals | |||||||
| Reduced Malondialdehyde & conjugated diene | |||||||
| Enhancement of glutathione, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase | |||||||
| Neuro-Hepato-Nephro Protective: | |||||||
| Spirulina’s enriched antioxidant profile helps to protect us from neuro-degenerative diseases like Alzhiemer’s, Parkinson’s and other forms of age related dementia. | |||||||
| Improves overall cognitive functions | |||||||
| Protects the liver and kidney cells from lipid peroxidation and ROS. | |||||||
| Protects liver and kidney cells from metal induced toxicity. | |||||||
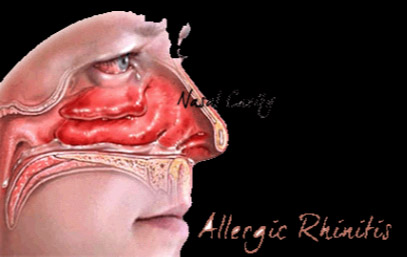
Allergy and Inflammation
| Anti-inflammatory effect of Spirulina | |||||||
| Decreasing leukotriene B4 & prostaglandin E2 in inflamed tissue | |||||||
| Significantly inhibits histamine release and TNF-α production mediated by IgE. | |||||||
| Alleviate the symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. | |||||||
| Relieve inflammation associated with Arthritis and various Allergies. | |||||||
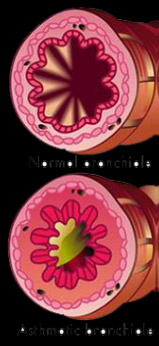
Spirulina and Asthma
| Beta-carotene, Vitamin E and Selenium content of Spirulina help in scavenging endogenous and/or environmental oxidant sources |
Spirulina and Skin Health
| Spirulina is very rich in β-carotene, which protects the skin by providing elasticity. | |||||||
| Together with vitamin E, Selenium and Zinc, β-carotene helps to deep cleanse the skin. | |||||||
| Chlorophyll in Spirulina is very beneficial for a healthy skin, due to its cell building factor and oxygen storing ability. | |||||||
| It is also beneficial against skin inflammations. | |||||||
| Gamma Linolenic acid (GLA) present in Spirulina protects the skin against UV radiation, dehydration and activates the blood circulation of the skin. | |||||||
| The high content of the natural amino acid like Tyrosine in Spirulina slows down the ageing process of cells. | |||||||
| It is also involved in the coloration of hair and skin, and helps with sun burn protection. | |||||||
| Vitamins presence is suitable as a nourishing moisturizer for dry older skin with under active sebaceous glands. Minerals are easily absorbed by the skin and are beneficial for an optimal function of the skin. | |||||||
| As a natural antioxidant, Vitamin E promotes the formation of skin cells, improves blood circulation and helps relieve symptoms of dermatitis and acne in teenagers (Moorhead et al., 1993; Tietze, 1999). |
Spirulina and Hypothyroidism
| Within the endocrine system, thyroid is the biological engine that ultimately directs hormonal function and, therefore, metabolism. Therefore, its proper functioning is critical to the body’s over all metabolic rate, energy (ATP) production, digestion, and many other functions. | |||||||||
| The elements most closely associated with the thyroid are: | |||||||||
| Iodine | |||||||||
| Tyrosine | |||||||||
| Selenium | |||||||||
| Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) consist of a tyrosine compound (made from the amino acid phenylalanine) to which atoms of iodine are added. | |||||||||
| Selenium is the most important nutrient required for the conversion of extra T4 to T3, as T3 is a more active form. | |||||||||
| Spirulina is having natural iodine and Selenium, which nourishes the thyroid, protects all glandular tissues and ultimately supports both immune and metabolic function. | |||||||||
| Phenylalanine present in it is used by the thyroid for the production of tyrosine (Triggiani et al., 2009; Kharrazian, 2010; Shames and Shames, 2002, Tietze, 1999). | |||||||||
Spirulina in Pregnancy & Overall Child development
| Spirulina is recommended for pregnant and nursing mothers as they need Spirulina’s extra easy-to-digest complete protein and bioavailable iron and folic acid. | |||||||
| Spirulina is also a source of essential fatty acids including DHA and EPA. | |||||||
| Moreover Spirulina is the only available plant source of vitamin-B12 and rich food source of GLA the main precursor to the body’s prostaglandins, the chemical which control many of body functions. (Umesh, 2002). | |||||||
| Spirulina high content of protein (56-69%) is easily digestible and available to body. | |||||||
| Sufficiently high intake of Spirulina may have potential for prevention and control of preeclampsia. | |||||||
| Intake of Spirulina is helpful in increasing fat content in milk of lactating mothers. | |||||||
| National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), Hyderabad has conducted several studies for Spirulina effect against anaemia and reports suggested that intake of Spirulina can plug iron deficiency among anaemic pregnant women. |
Weight Management
| Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina can be used for weight management. | |||||||
| It is low in calories, fat, highly digestible and what is very important, it is in its natural balance | |||||||
| Spirulina contains both Tyrosine and Phenylalanine, which directly influence the neurotransmitters (norepinephrine and dopamine) in brain which control appetite | |||||||
| It is a rich source of GLA, which has a specific effect on the endocrine system, helping restore hormone, health and prevents insulin resistance, which is one of the cause of Obesity in diabetic patients. |
Anticancer and Antiviral properties of Spirulina
| Anticancer properties of Spirulina are due to high content of Phycocyanin present in it. | |||||||
| Phycocyanin enriched Spirulina induces apoptosis in tumour cells by fragmentising damaged DNA. | |||||||
| The unique polysaccharides of Spirulina improve the immune system to combat against cancerdrug resistance. | |||||||
| Spirulina has shown antiviral effects in laboratory and animal studies. It appeared to block the entrance of viral cells in to host cells. | |||||||
| Several viruses, including HIV- the virus that causes AIDS – were apparently killed or damaged by Spirulina or chemicals (cyanovirin-N protein) derived from it. |




